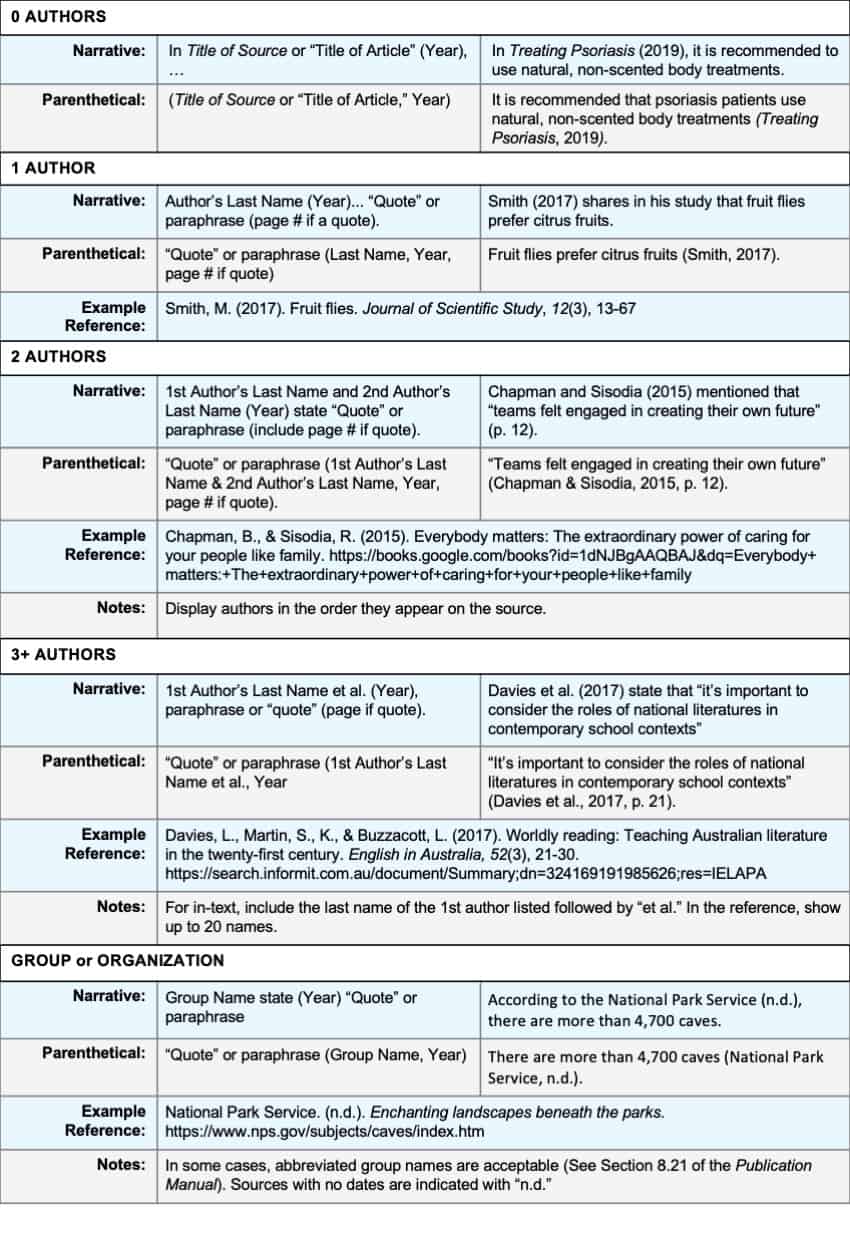
Welcome to a comprehensive guide on citing sources and formatting papers in the American Psychological Association style. Below are reference and in-text citation examples, directions on formatting your paper, and background information on the style.
APA stands for the American Psychological Association, which is an organization that focuses on psychology. They are responsible for creating this specific citation style. They are not associated with this guide, but all of the information here provides guidance to using their style and follows the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association.
APA style is used by many scholars and researchers in the behavioral and social sciences, not just psychology. There are other citation formats and styles such as MLA and Chicago citation style, but this one is most popular in the fields of science.
Following the same standard format for citations allows readers to understand the types of sources used in a project and also understand their components.
The information in this guide follows the 7th edition of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association. It outlines proper ways to organize and structure a research paper, explains grammar guidelines, and how to properly cite sources. This webpage was created solely by BibMe to help students and researchers focus on how to create APA citations.
The 7th edition of the Publication Manual was released in 2020. We address differences between the 6th and 7th editions at the end of this guide.
For more information, please consult the official Publication Manual.
We cite sources for many reasons. One reason is to give credit to the authors of the work you used to help you with your own research. When you use another person's information to help you with your project, it is important to acknowledge that individual or group. This is one way to prevent plagiarism. Another reason why we create citations is to provide a standard way for others to understand and possibly explore the sources we used. To learn more about citations, check out this page on crediting work. Also, read up on how to be careful of plagiarism.
There are two types of citations:
Depending on the types of sources used for your project, the structure for each citation may look different. There is a certain format or structure for books, a different one for journal articles, a different one for websites, and so on. Scroll down to find the appropriate APA format structure for your sources.
Even though the structure varies across different sources, see below for a full explanation of in-text citations and reference citations.
Still wondering, "What is APA format?" To learn more about APA referencing, including access to the American Psychological Association\'s blog, formatting questions, & referencing explanations, click on this link for further reading on the style. To learn more about using the BibMe service (BibMe.com) to help build APA citation website references, see the section below titled, "Using the BibMe Online Writing Center to Create Citations for your Reference List or APA Bibliography."
When using a direct quote or paraphrasing information from a source, include an in-text or parenthetical citation into the body of your project, immediately following it.
An APA in-text citation may look similar to this:
Author's Last name (Year) states that "direct quote" or paraphrase (page number).
Parenthetical citations look like this:
"Direct quote" or paraphrase (Author's Last name, Year, Page number).
These types of APA citations always have the author and the date together.
Only direct quotes need a page number. For paraphrased information, it isn't necessary, but helpful for the reader.
See the section below titled, "In-Text or Parenthetical Citations," for a full explanation and instructions.
Each source used in your project is listed as a full citation on the APA reference page, which is usually the last part of a project.
The structure for each citation is based on the type of source used. Scroll down to see APA format examples of some common source formats.
Most print and offline citations include the following pieces of information, commonly in this order:
Author's Last name, First initial. Middle initial. (Date published). Title of source. Publisher.
Most online citations include the following pieces of information, commonly in this order:
Author's Last name, First Initial. Middle initial. (Date published). Title of source. URL
To see how to format each section, scroll down to the appropriate areas of this guide. There is a section on authors, one on publication dates, another on titles, publishers, and on online information.
To determine the exact APA citation format for your full citations, scroll down to the section titled, "Common Examples."
For a detailed explanation on formatting your reference list, scroll down to the section titled, "Your Reference List."
All in-text citations included throughout the paper should have a corresponding full reference at the end of the project.
Full references go on their own page at the end of a project. Title the page "References"
References are listed in alphabetical order by the first word in the reference (usually the author's last name, sometimes the title).
If you're looking for an easy way to create your references and citations, use BibMe's free APA citation machine, which automatically formats your sources quickly and easily.
Authors are displayed in reverse order: Last name, First initial. Middle initial. End this information with a period.
APA format example:
Kirschenbaum, M. A.
In an APA citation, include all authors shown on a source. If using the BibMe APA citation builder, click "Add another contributor" to add additional author names. Our free citation creator will format the authors in the order in which you add them.
Multiple authors, same last name:
If your reference list has multiple authors with the same last name and initials, include their first name in brackets.
Example:
Brooks, G. [Geraldine]. (2005). March. Viking.
Brooks, G. [Gwendolyn]. (1949). Annie Allen. Harper & Brothers.
No author:
When no author is listed, exclude the author information and start the citation with the title followed by the year in parentheses.
Editors:
When citing an entire edited book in APA format, place the names of editors in the author position and follow it with Ed. or Eds. in parentheses. See below for examples of citing edited books in their entirety and also APA citation format for chapters in edited books.
Comparison chart:
Use this handy chart to determine how to format author names in citations and references.

General structure is:
Place the date that the source was published in parentheses after the name of the author. In APA format for periodicals, include the month and day as well. If no date is available, place n.d. in parentheses, which stands for no date. For more details, see Section 9.14 of the Publication Manual.
For book titles: Only capitalize the first letter of the first word in the title and the same for the subtitle. Capitalize the first letter for any proper nouns as well. Place this information in italics. End it with a period.
Example:
Gone with the wind.
For articles and chapter titles: Only capitalize the first letter of the first word in the title and the same for the subtitle. Capitalize the first letter for any proper nouns as well. Do not italicize the title or place it in quotation marks. End it with a period.
Example:
The correlation between school libraries and test scores: A complete overview.
For web pages on websites: Same as above. The web page title is italicized.
Example:
Simmons, B. (2015, January 9). The tale of two Flaccos. Grantland. http://grantland.com/the-triangle/the-tale-of-two-flaccos/
For magazine, journal, and newspaper titles: Each important word should start with a capital letter.
Example:
The Boston Globe
If you believe that it will help the reader to understand the type of source, such as a brochure, lecture notes, or an audio podcast, place a description in brackets directly after the title. Only capitalize the first letter.
Example:
New World Punx. (2014, February 15). A state of trance 650 [Audio file]. https://soundcloud.com/newworldpunx/asot650utrecht
Publisher Location
In previous editions of the publication manual, books and sources that were not periodicals indicated the city and state of publication. However, in the 7th edition, the location of publication is no longer given except “for works associated with specific locations, such as conference presentations” (p. 297).
For conference presentations, give the city, state/province/territory, and country. If in the US, abbreviate the state name using the two-letter abbreviation. Place a colon after the location.
Examples:
Periodical Volume and Number
For journals, magazines, newspapers, and other periodicals, place the volume number after the title. Italicize this information. Place the issue number in parentheses and do not italicize it. Afterwards, include page numbers.
Example:
Journal of Education for Library and Information Science, 57(1), 79-82.
If you're citing a newspaper article, include p. or pp. before the page numbers.
The names of publishers are not necessary to include for newspapers, magazines, journals, and other periodicals.
For books and other sources: It is not necessary to type out the name of the publisher exactly as it is shown on the source. Use a brief, but understandable form of the publisher's name. Exclude the terms publishers, company, and incorporated. Include Books and Press if it is part of the publisher's name. End this information with a period (See Section 9.29 in the Publication manual for more details).
Example:
Little Brown and Company would be placed in the APA citation as: Little Brown.
Oxford University Press would be placed in the citation as: Oxford University Press.
For sources found online:
If you're citing a periodical article found online, there might be a DOI number attached to it. This stands for Direct Object Identifier. A DOI, or digital object identifier, is a unique string of numbers and letters assigned by a registration agency. The DOI is used to identify and provide a permanent link to its location on the Internet. The DOI is assigned when an article is published and made electronically. If your article does indeed have a DOI number, use this instead of the URL as the DOI number is static and never changes. If the source you're citing has a DOI number, after the publication information add a period and then http://dx.doi.org/10.xxxx/xxxxxx. The x's indicate where you should put the DOI number. Do not place a period after the DOI number. See sections 9.35-36 in the Publication manual for more details.
If you're using the automatic BibMe APA reference generator, you will see an area to type in the DOI number.
Example:
Lobo, F. (2017, February 23). Sony just launched the world's fastest SD card. http://mashable.com/2017/02/23/sony-sf-g-fastest-sd-card/?utm_cid=mash-prod-nav-sub-st#ErZKV8blqOqO
Chadwell, F.A., Fisher, D.M. (2016). Creating open textbooks: A unique partnership between Oregon State University libraries and press and Open Oregon State. Open Praxis, 8(2), 123-130. http://dx.doi.org/10.5944/openpraxis.8.2.290
Looking for more help and clarification? Check out this great resource!
Author's Last name, First name initial. Middle name initial. (Year published). Title of book. Publisher.
Example:
Finney, J. (1970). Time and again. Simon and Schuster.
Looking for an APA formatter? Don't forget that the BibMe APA citation generator creates citations quickly and easily.
Notes: When creating an APA book citation, keep these in mind:
Most edited books state on the cover or title page that they are edited by an author or multiple authors. The format is the same as a print book, except the editor's name is in the author's position. Include a parentheses afterwards with the abbreviation (Ed.) for an edited book by one author or (Eds.) for an edited book with two or more authors.
Editor, F. M. (Ed.). (Year published). Title of edited book. Publisher.
Example:
Gupta, R. (Ed.). (2003). Remote sensing geology. Springer-Verlag.
Some edited books contain chapters written by various authors. Use the format below to cite an author's individual chapter in an edited book.
Chapter author's Last name, F. M. (Year published). Title of chapter. In F. M. Last name of Editor (Ed.), Title of book (p. x or pp. x-x). Publisher.
Notice that for APA style, the title of the chapter is not italicized, while the title of the book is. In addition, the chapter author's name is reversed at the beginning of the reference, but the editor's name is written in standard order.
Example:
Longacre, W. A., & Ayres, J. E. (1968). Archeological lessons from an Apache wickiup. In S. R. Binford & L. R. Binford (Eds.), Archeology in cultural systems (pp. 151-160). https://books.google.com/books?id=vROM3JrrRa0C&lpg=PP1&dq=archeology&pg=PR9#v=onepage&q=archeology&f=false
In the above example, Longacre and Ayers are the authors of the individual chapter and Binford & Binford are the editors of the entire book.
E-book is short for "electronic book." It is a digital version of a book that can be read on a computer, e-reader (Kindle, Nook, etc.), or other electronic devices. Include the DOI or URL if one exists for the e-book.
Author's Last name, F. M. (Year published). Title of work. https://doi.org/10.xxxx/xxxxxx or URL
https://doi.org/10.xxxx/xxxxxx is used when a source has a DOI number. If the e-book you're citing has a DOI number, use it in the APA citation. DOIs are preferred over URLs.
How to cite in APA (an e-book example):
Eggers, D. (2008). The circle. https://www.amazon.com
Use this format when citing an e-book that is either found on a website, or found on a subscription database. APA formatting for this is very similar to the structure of a print book. The only difference? Instead of the publisher information, include the DOI number or URL.
Author's Last name, F. M. (Year published). Title of work. https://doi.org/10.xxxx/xxxxxx OR URL
When citing an online book or e-book, keep in mind:
Example:
Sayre, R. K., Devercelli, A. E., Neuman, M. J., & Wodon, Q. (2015). Investment in early childhood development: Review of the world bank's recent experience. https://doi.org/10.1596/978-1-4648-0403-8
Need to cite a chapter in an e-book? No problem! Citing a chapter in an e-book is very similar to citing a chapter in a print book. Instead of including the publisher information, include a DOI number (if one is displayed) or the URL.
Chapter author's Last name, F. M. (Year published). Title of chapter. In F. M. Last name of Editor (Ed.), Title of book (p. x or pp. x-x). https://doi.org/10.xxxx/xxxxxx or URL
Epstein W. M. (1999). The ineffectiveness of psychotherapy. In C. Feltham (Ed.), Controversies in psychotherapy and counselling (pp. 65-73). https://doi.org/10.4135/9781446217801.n8
How to cite a web page on a website in APA:
Author's Last name, F. M. (Year, Month Day published). Title of article or page. Site Name. URL
APA website citation example:
Simmons, B. (2015, January 9). The tale of two Flaccos. Grantland. http://grantland.com/the-triangle/the-tale-of-two-flaccos/
Citing a web page with a group author:
Group Name. (Year, Month Date published). Title of wep page. Saite Name included if different from Group Name. URL
Examples:
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2020, February 3). Be prepared to stay safe and healthy in winter. https://www.cdc.gov/features/winterweather/index.html
National Park Service. (n.d.). Enchanting landscapes beneath the parks. https://www.nps.gov/subjects/caves/index.htm
Note: "n.d." stands for "no date" and is used when there is no publication date.
The above follows Section 10.16 of the Publication manual.
Still wondering how to cite a website in APA? Check out BibMe.com! It's quick, simple, and free! Our APA citation machine also builds references for many other styles as well!
Today, most journal articles are found online, but you may be lucky enough to score a copy of a print version for your research project. If so, use the structure below for your reference:
Author's Last name, F. M. (Year published). Article title. Periodical Title, Volume(Issue), pp.-pp.
Notice that the article's title is only capitalized at the beginning. If there are any proper nouns or subtitles, capitalize the first letter for those words as well. The journal article's title and the volume number are both italicized. In addition, the title of the journal is in title case form (all important words are capitalized).
Example:
Nevin, A. (1990). The changing of teacher education special education. Teacher Education and Special Education: The Journal of the Teacher Education Division of the Council for Exceptional Children,13(3-4), 147-148.
Databases are a popular place to find high quality journal articles. These references are formatted the same way as the print versions, except the DOI or URL is included at the end. If the article has a corresponding DOI number, use it instead of the URL. No URL? Use the homepage of the journal's website for the URL. See Section 10.1 in the Publication manual for additional examples.
Author's Last name, F. M. (Year published). Title of article. Title of Journal, volume number(issue number), page range. https://doi.org/10.xxxx/xxxxxx OR URL
Example:
Spreer, P., & Rauschnabel, P. A. (2016). Selling with technology: Understanding the resistance to mobile sales assistant use in retailing. Journal of Personal Selling & Sales Management, 36(3), 240-263. https://doi.org/10.1080/08853134.2016.1208100
Notes: When creating your online journal article citation, keep in mind:
Similar to journal articles, most individuals use online newspaper articles for research projects. However, if you're able to get your hands on a print version, use this structure for your reference:
Author's Last name, F. M. (Year, Month Day of Publication). Article title. Newspaper Title, pp. xx-xx.
Example:
Rosenberg, G. (1997, March 31). Electronic discovery proves an effective legal weapon. The New York Times, p. D5.
Notes: When creating your newspaper citation, keep in mind:
Use this structure when referencing a newspaper article found on a website or database:
Author's Last name, F. M. (Year, Month Day of Publication). Title of article. Title of Newspaper. URL of newspaper's homepage
Example:
Rosenberg, G. (1997, March 31). Electronic discovery proves an effective legal weapon. The New York Times. http://www.nytimes.com
Notes: When citing a newspaper, keep in mind:
Citing a magazine article in print:
Author's Last name, F. M. (Year, Month of publication). Article title. Magazine Title, Volume(Issue), page range.
APA format citation:
Tumulty, K. (2006, April). Should they stay or should they go? Time, 167(15), 3-40.
Notes: When citing a magazine, keep in mind:
Citing a magazine article found online:
Author's Last name, F. M. (Year, Month of publication). Article title. Magazine Title, Volume(Issue). URL
Example:
Tumulty, K. (2006, April). Should they stay or should they go? Time, 167(15). http://content.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,1179361,00.html
Notes: When creating an online magazine citation, keep in mind:
*The volume and issue number aren't always on the same page as the article. Check out the other parts of the website before leaving it out of the citation.
Blogs are found on websites and display continuously updated content and posts by a single author, group, or company. A blog shows news updates, ideas, information, and many other types of entries. Similar to journal entries, a blog begins with the date the information was added followed by the content.
If you’re wondering how to cite a blog entry, look no further! Citing a blog is very similar to citing a website.
Citing a blog post:
Last name of Author, First initial. Middle initial. (Year, Month Day blog post was published). Title of blog post. Title of Blog. URL
Example:
Gonzalez, J. (2019, February 3). Let’s give our teaching language a makeover. Cult of Pedagogy. https://www.cultofpedagogy.com/language-makeover/
Notice that the blog title only has a capital letter at the beginning. If there are any proper nouns in the title, capitalize the first letter for those as well.
Cite a blog post in the text of the paper:
(Author’s last name, Year)
Author’s last name (Year)
A research, or technical report, is a piece of work that provides insight into research done by an individual researcher, a group of researchers, or a company or organization.
Citing a research report in print:
Author’s Last Name, F. M. or Organization. (Year published). Title of research report (Report No.). Publisher.
Note: If the publisher is the same as the author, use the name as the the “Author” and don't list the publisher.
Example:
Michigan Venture Capital Association. (2018). Annual research report.
Citing an online research report:
Author’s Last Name, F. M. or Organization. (Year published). Title of research report (Report No.). URL
Example:
Newson, S. E. & Berthinussen, A. (2019). Improving our understanding of the distribution and status of bats within the Ryevitalise Landscape Partnership Scheme area (BTO Research Report No. 716). https://www.bto.org/sites/default/files/publications/btorr716finalwebsite.pdf
Producer's Last name, F. M. (Producer), & Director's Last name, F. M. (Director). (Release Year). Title of motion picture [Motion picture]. Studio.
Example:
Bender, L. (Producer), & Tarantino, Q. (Director). (1994). Pulp fiction [Film]. Miramax.
Citations for Online Films & Videos:
Person who posted the video's Last name, F. M. [User name]. (Year, Month Day of posting). Title of video [Video]. Publishing site. URL
If the name of the individual who posted the YouTube video is not available, begin the citation with the user name and do not place this information in brackets.
Smith, R. [Rick Smith] (2013, September 20). Favre to Moss! [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gOP_L6hBjn8
Note: If you're discussing a certain part of the film or video in the body of your project, include a timestamp in the in-text or parenthetical citation. (Pulp Fiction, 1994, 1:15:30). The time stamp is Hours:Minutes:Seconds.
Citing an image found in a print publication (such as a book or magazine) or museum:
Creator's Last name, F. M. (Year of Publication). Title of image [Format]. Publisher/Museum.
Including the format helps the reader understand and visualize the type of image that is being referenced. It can be [Photograph], [Painting], or another medium.
Example:
Roege, W. J. (1938). St. Patrick's Cathedral, Fifth Avenue from 50th St to 51st Street [Photograph]. New York Historical Society.
Citing an image retrieved online:
Similar to citing an image in print, when citing an image found online, place the medium, or format, in the brackets. Capitalize the first letter.
Photographer, F. (Year of Publication). Title of photograph [Photograph]. Publisher. URL
Example:
Ferraro, A. (2014). Liberty enlightening the world [Digital image]. Flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/afer92/14278571753/in/set-72157644617030616
Writer's Last name, F. M. (Writer), & Director's Last name, F. M. (Director). (Year of Airing). Episode title [TV series episode]. In F. M. Executive Producer's Last name (Executive Producer), TV series name. Channel.
Kand, K. (Writer), & Fryman, P. (Director). (2006). Slap bet [TV series episode]. In C. Bays (Executive Producer), How I met your mother. CBS.
TV/Radio Broadcasts found online:
Writer, F. M. (Writer), & Director, F. M. (Director). (Year of Airing). Episode title [Television series episode]. In F. M. Executive Producer's Last name (Executive Producer), TV series name. URL
Kand, K. (Writer), & Fryman, P. (Director). (2006). Slap bet [Television series episode]. In C. Bays (Executive Producer), How I met your mother. https://www.hulu.com/watch/1134858#i0,p30,d0
Note: When citing a TV show or episode, keep in mind:
Type what you find into the BibMe APA formatter. We'll do the work for you and structure your references properly!
To cite in APA a song from an album listened to online, use the following structure:
Songwriter's Last name, F. M. (Copyright year). Title of song [Song recorded by F. M. Last name]. On Album title. Publisher. URL
Swift, T. (2008). Love Story [Song]. On Fearless. Big Machine Records.
If you're using the BibMe APA citation generator to build your references, choose "Music/Audio" from the source options.
A personal interview should NOT be included in a reference list. They are not considered recoverable data (they cannot be found by a researcher). You should reference personal interviews as citations in the body of the project instead.
Example:
(J. Doe, personal communication, December 12, 2004)
Encyclopedia/Dictionary in print:
Author's Last name, F. M. (Publication Year). Entry title. In F. M. Last name of Editor (Ed.), Title of encyclopedia or dictionary (pp. xx-xx). Publisher.
Example:
Kammen, C., & Wilson, A. H. (2012). Monuments. Encyclopedia of local history. (pp. 363-364). AltaMira Press.
Encyclopedia/Dictionary online with author(s):
Author’s Last name, F. M. (Publication Year or n.d.). Entry title. In F. M. Last name of Editor (Ed.), Title of encyclopedia or dictionary. Publisher. Retrieved date, from URL
Encyclopedia/Dictionary online with group author:
Publisher or group name (Publication Year or n.d.). Entry title. In Title of encyclopedia or dictionary. Retrieved date, from URL
Example:
Merriam-Webster. (n.d.). Taciturn. In Merriam-Webster.com dictionary. Retrieved February 10, 2020, from https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/taciturn
If an entry looks like it goes through many updates, use “n.d.” as the publication date and show the date you retrieved it. If using an archived version, no retrieval date is needed.
This style of reference would be used if you were citing a set of notes from a lecture (e.g., PowerPoint or Google slides provided by your instructor).
Citing online lecture notes or presentation slides:
Author's Last name, F. M. (Publication year). Name or title of lecture [Lectures notes or PowerPoint slides]. URL
Example:
Saito, T. (2012). Technology and me: A personal timeline of educational technology [PowerPoint slides]. http://www.slideshare.net/Bclari25/educational-technology-ppt
Tip: If you want to cite information from your own personal notes from a lecture, this is considered personal communication. The notes may not be available online for others outside of the class to access. Refer to it only in the body of your essay or project. You can follow the style guide for personal communication available in the Interview section.
Social media is everywhere, even in research projects. Many influencers post thoughts, inspirational quotes, and intriguing stories in their profiles.
If you need to cite a post from a social media platform, use this structure:
Last name, F. M. or Group Name who posted the content [@Username]. (Year, Month Day posted). First 20 words of the post [Format]. Social Media Site Name. URL
Last name, F. M. or Group Name who posted the content [@Username]. (Year, Month Day posted). First 20 words of the post [Format]. Social Media Site Name. URL
A retrieval date (date you saw the page) is needed for profile pages since the contents are likely to change over time (e.g., Instagram profile, Facebook page etc.). The structure for that is:
Last name, F. M. or Group Name who posted the content [@Username]. (n.d.). Tweets or Home [Format]. Social Media Site Name. Retrieved from month day, year, URL
Some things to keep in mind:
Citing a Tweet from Twitter:
BibMe [@BibMe]. (2020, January 22). How to cite primary sources ow.ly/fUb950vG3N5 [Tweet]. Twitter. https://twitter.com/bibme/status/1219976780746043392
Citing a Twitter profile:
BibMe [@BibMe] (n.d.). Tweets [Twitter profile]. Twitter. Retrieved February 18, 2020, from https://twitter.com/BibMe
Citing a Facebook post:
DeGeneres, E. (2018, December 21). Holiday party goals [Facebook status update]. Facebook. https://www.facebook.com/ellentv/photos/a.182755292239/10157188088077240/?type=3&theater
Citing a Facebook page:
Smithsonian’s National Zoo and Conservation Biology Institute. (n.d.) Home [Facebook page]. Facebook. Retrieved July 22, 2019, from https://www.facebook.com/nationalzoo
Citing an Instagram post:
Lipa, D. [@dualipa]. (2018, December 2). A lil Hollywood glam brunch! Thank you @variety for by Breakthrough Artist of the Year award and thank you for [Instagram photo]. Instagram. https://www.instagram.com/p/Bq33SC2BAsr/?utm_source=ig_web_copy_link
Since this citation style is commonly used in science-related disciplines, it makes sense that many students and scholars include tables in their projects.
It's a good idea to include a table in your project when:
Do not write out the information from the table in the text of your paper. Including the same information in two spots is repetitive. Either type out the quantitative information in your paper or use a table.
If you choose to include a table, make sure to:
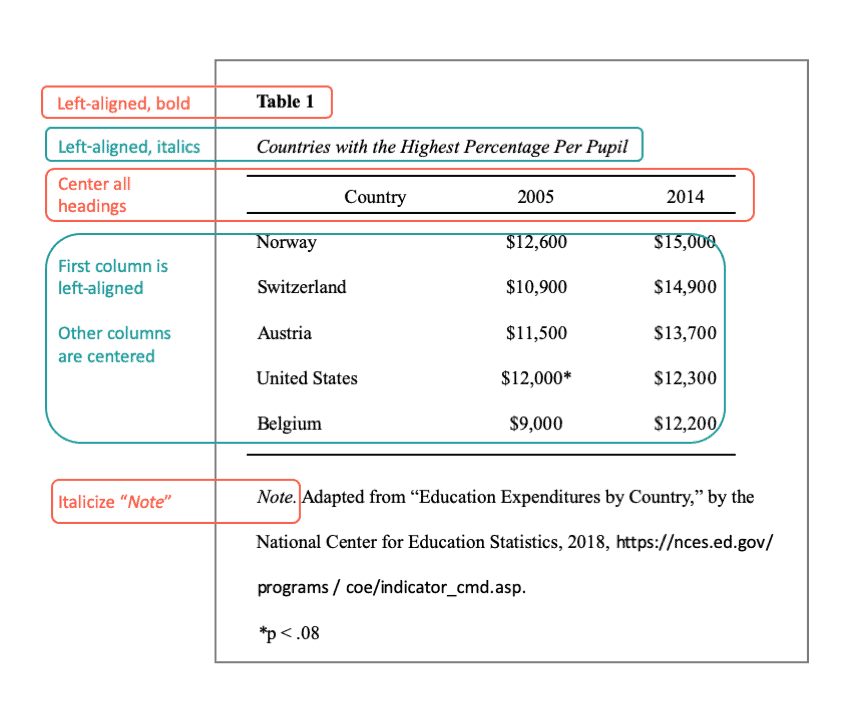
Prior to adding your table into your paper, use this handy checklist to confirm you have all of the requirements:
__ Is it necessary to include the table?
__ Are only horizontal lines included?
__ Did you include a simple, straightforward title? Is it in italics?
__ Did you use either single spaces or double spaces? APA paper format requires you to keep your tables consistent across your project.
__ Are column headings included?
__ Are notes included below the table to provide understanding? Are the notes in the proper order? Start with general notes, then include specific notes, and end with probability notes.
__ Did you refer to the table in the written portion of your paper?
Still have questions? See Chapter 7 of the Publication manual.
The purpose of in-text and parenthetical citations is to give the reader a brief idea as to where you found your information, while they're in the middle of reading or viewing your project. You may include direct quotes in the body of your project, which are word-for-word quotes from another source. Or, you may include a piece of information that you paraphrased in your own words. These are called parenthetical citations. Both direct quotes and paraphrased information include a citation next to it. You also need to include the full citation for the source in the reference list, which is usually the last item in a project.
In-text and parenthetical citations are found immediately following any direct quotes or paraphrases. They should include the page number or section information to help the reader locate the quote themselves.
Example:
Buck needed to adjust rather quickly upon his arrival in Canada. He stated, "no lazy, sun-kissed life was this, with nothing to do but loaf and be bored. Here was neither peace, nor rest, nor a moment's safety" (London, 1903, p. 25).
When taking an idea from another source and placing it in your own words (a paraphrase), it is not necessary to include the page number, but you can add it if the source is large and you want to direct readers right to the information.
Example:
At the time, papyrus was used to create paper, but it was only grown and available in mass quantities in Egypt. This posed a problem for the Greeks and Romans, but they managed to have it exported to their civilizations. Papyrus thus remained the material of choice for paper creation (Casson, 2001).
An in-text citation in APA displays the author's name directly in the sentence, or text, of the paper. Always place the year directly after the author's name. Authors and dates stick together like peanut butter and jelly! If you're citing a direct quote, place the page number at the end of the quote.
Parenthetical citations display the author's name and year in parentheses after a quote or paraphrase. If you're citing a direct quote, include the page number as well. If you're paraphrasing, it is up to you whether or not you'd like to include a page number.
Example of various ways to cite in the body of a project:
Smith (2014) states that, "the Museum Effect is concerned with how individuals look at a work of art, but only in the context of looking at that work along with a number of other works" (p. 82).
"The Museum Effect is concerned with how individuals look at a work of art, but only in the context of looking at that work along with a number of other works" (Smith, 2014, p. 82).
If your source has two authors, always include both names in each in-text or parenthetical citation.
Example: (Franks & Beans, 2019)
If your source has three or more authors, only include the first author's name and follow it with et al.
Example: (Gilley et al., 2015)
If your source was written by a company, organization, government agency, or other type of group, include the group's name in full in the first in text or parenthetical citation. In any APA citations following it, it is acceptable to shorten the group name to something that is simple and understandable.
Example:
1st citation:
2nd and subsequent citations:
Still wondering how to in-text cite in APA? How about citing parenthetically? Check out this page to learn more about parenthetical citations. Also, BibMe writing tools can help create your in-text and parenthetical citations quickly and easily. Towards the end of creating a full reference citation, you'll see the option to create a citation for the body of your project (in-text) in the APA format generator.
Need help with your writing? Give the BibMe Plus paper checker a whirl! Upload your paper or copy and paste it into the text box on the page. We'll run it through our innovative technology and let you know if there is an adjective, verb, or pronoun out of place, plus much, much more!
The listing of all sources used in your project are found in the reference list, which is the last page or part of a project. Included in this reference list are all of the sources you quoted or paraphrased in the body of your paper. This means that every reference found in the reference list should have a matching in-text or parenthetical citation in your project. Where there is one, there has to be the other. Here are general guidelines:
Example:
Thompson, H. S. (1971). Fear and loathing in Las Vegas: A savage journey to the heart of the American dream. Random House.
Thompson, H. S. (1998). The rum diary. Simon & Schuster.
If there are multiple sources with the same author AND same publication date, place them in alphabetical order by the title.
Example:
Dr. Seuss. (1958). The cat in the hat comes back. Random House.
Dr. Seuss. (1958). Yertle the turtle. Random House.
If a source does not have an author, place the source in alphabetical order by the first main word of the title.
Need help creating the citations in your APA reference list? BibMe.com helps you generate citations! Begin by entering a keyword, URL, title, or other identifying information. Try it out!
Sample Reference List:

Here's more information with sample papers and tutorials. Further information acan be found in Chapter 9 of the Publication manual.
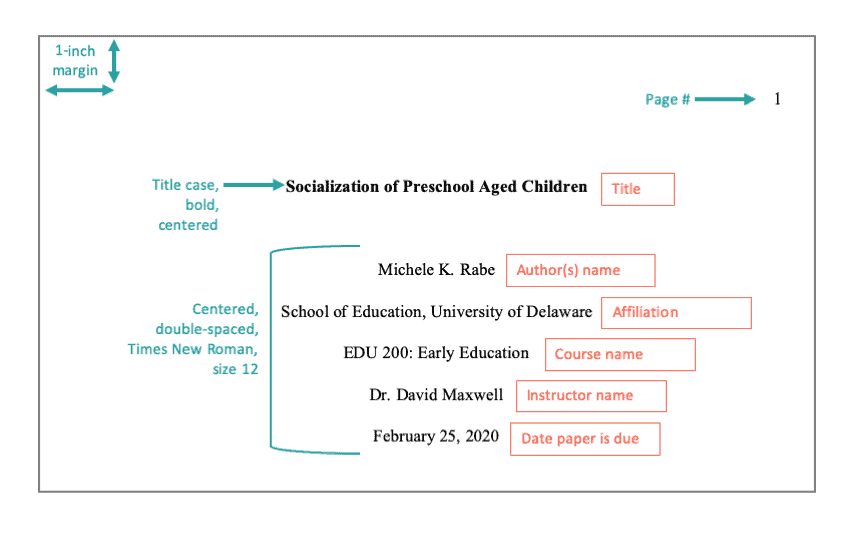
Need to create APA format papers? Follow these guidelines:
In an APA style paper, the font used throughout your document should be in Times New Roman, 12 point font size. The entire document should be double spaced, even between titles and APA headings. Margins should be 1 inch around the entire document and indent every new paragraph using the tab button on your keyboard. See Chapter 2 of the Publication manual for more details on paper formatting.
Place the pages in the following order:
Page numbers: The title page counts as page 1. Number subsequent pages using Arabic numbers (1, 2, 3, 4. ).
Your title page should grace the front cover of your paper. It's sometimes called an APA cover page. Included on this page are seven items:
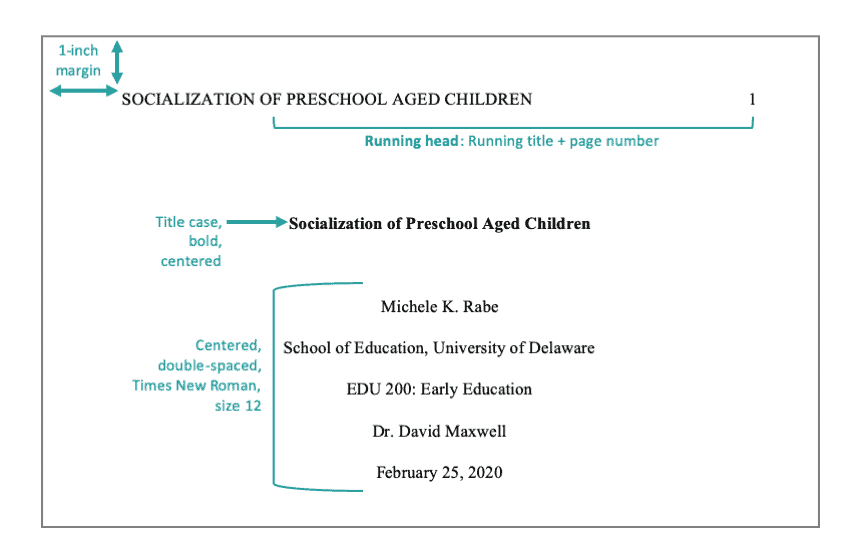
What is a running head?
The running head shows the title of your paper. It is only required for professional papers (e.g., dissertations, journal submissions, etc.).
Student papers do not need a running head (but do need the page number).
If you use one, place the running head in the top left corner of your project and place it in capital letters. Use your word processor's "header" option. It will automatically place your running head in the appropriate position, against the left margin.
Across from the running head, against the right margin, include the page number. The APA title page is 1.
Title page example:
Microsoft Word, Google Docs, and many other word processing programs allow you to set up page numbers and a repeated running head. Use these tools to make this addition easier for you!
Need help determining the title of your paper? Keep it simple and straight to the point. Exclude unnecessary terms such as "An Analysis of. " or "A Study of. " If your paper ends up being digitized and added to your school's research collection or a research database, a simple and effective title will help researchers locate it. It is recommended to keep it under 12 words and avoid abbreviations.
Order | Element | Format & Notes --- | --- | --- 0 | All elements, except page number | Centered, double-spaced lines 1 | Page number | Place “1” in the upper right corner of the page. Professional papers only: Include a running head. 2 | Title of paper | 3-4 lines from the top of the page; bolded, and title case 3 | Name of author(s) | Two double-spaced lines under the title. No font formatting (no bold italics, underline). Exclude any titles (such as Dr. or Ms.) and degrees (such as PhD). List all contributors; if there is more than one include the word “and” between the second to last and last names. 4 | Affiliation (school, department, etc.) | No font formatting. Usually includes the name of your department and university. 5 | Course name | No font formatting. Write the course name and number on your class materials: ENG 102, JPN301. 6 | Instructor | No font formatting. Show their name as they prefer, including titles and degrees. 7 | Date paper is due | Month Day, Year. Example: February 14, 2020
Example Title Page - Student Paper:
Example Title Page - Professional Paper:
If you're looking for an APA sample paper, check out the other resources found on BibMe.com.
Levels of Headings:
There are a lot of rules to follow when it comes to styling the header and title page, but there are even more rules when it comes to styling the various headings and sections in your research paper.
There are five sizes and styles, and they follow a top down approach.
In most cases, science-related papers and case studies have three sections: Method, Results, and Discussion. These three sections are considered “Level 1” and are aligned in the center of the page and in bold. Additional sections of the paper are styled as follows:
Overview of Levels
Level | Formatting --- | --- 1 | Center and bold. Use title case. 2 | Against the left margin and in bold. Use title case. Begin the next sentence on the next line, indented half an inch from the left margin. 3 | Against the left margin in bold and italics. Use title case. Begin your next sentence on the next line, and indented half an inch from the left margin. 4 | Indented half an inch from the left. Is in bold. Use title case. Begin your next sentence on the same line and immediately following the heading. 5 | Indented half an inch from the left. Is in bold and italics. Use title case. Begin your next sentence on the same line and immediately following the heading.
We’ve included a visual below to help you make sense of the five headings. Keep in mind, you do not need to have all five headings in your paper. You may only use the top two or three. It depends on the types of sections your paper includes.

Looking to cite your sources quickly and easily? BibMe can help you generate your citations; simply enter a title, ISBN, URL, or other identifying information.
Click to see more styles, and if you'd like to cite your sources in MLA format, check out the BibMe MLA page. Other citation styles are available as well.
Not only will BibMe help you create your references quickly and painlessly, we'll also scan your paper with an innovative plagiarism checker. BibMe writing tools even helps to check your grammar, too! Improper usage of adverb? Missing an interjection? Determiner out of place? BibMe writing tools will highlight any areas of concern and offer suggestions to improve your writing. Try it out now!
The American Psychological Association was founded in 1892 at Clark University in Worcester, Massachusetts. APA style format was developed in 1929 by scholars from a number of different scientific fields and backgrounds. Their overall goal was to develop a standard way to document scientific writing and research.
Since its inception, the Style Manual has been updated numerous times and it is now in its 7th edition (2020). The previous 6th edition was released in 2009. In 2012, APA published an addition to their 6th edition manual, which was a guide for creating an APA style citation for any type of electronic resource.
Today, there are close to 118,000 members. There is an annual convention, numerous databases, and journal publications. Some of their more popular resources include the database, PsycINFO, and the publications, Journal of Applied Psychology and Health Psychology.
Below is a selection of notable citing differences between the two editions.
For journal articles with a DOI number, include the DOI as a URL.
6th edition example:
Lee, C.-H., & Mackinnon, R. (2019). Voltage sensor movements during Hyperpolarization in the HCN Channel. Cell Studies. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.11.006
7th edition example:
Lee, C.-H., & Mackinnon, R. (2019). Voltage sensor movements during Hyperpolarization in the HCN Channel. Cell Studies. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2019.11.006
For ebooks, you no longer need to identify the format.
6th edition example:
Murakami, H. (2014). Kafka on the shore [Kindle].
7th edition example:
Murakami, H. (2014). Kafka on the shore.
Full book references no longer need to show where the publisher is located.
6th edition example:
Murakami, H. (2014). Kafka on the shore. London: Vintage Publishing.
7th edition example:
Murakami, H. (2014). Kafka on the shore. Vintage Publishing.
In-text citations for sources with more than 3 authors can use the notation “et al.” for brevity.
(first author’s name et al., year published)
6th edition example:
(Anaydike, Braga, Talfah, Gonzalez, 1980)
7th edition example:
When including a website URL, do not include the words “Retrieved from” before the URL cited.
6th edition example:
Elan, P. (2019, December 6). 'A reflection of inner life': show explores history of the hoodie. The Guardian. Retrieved from https://www.theguardian.com/fashion/2019/dec/06/a-reflection-of-inner-life-show-explores-history-of-the-hoodie
7th edition example:
Elan, P. (2019, December 6). 'A reflection of inner life': show explores history of the hoodie. The Guardian. https://www.theguardian.com/fashion/2019/dec/06/a-reflection-of-inner-life-show-explores-history-of-the-hoodie
The citing format for tables and figures are now the same. For both, indicate a table number and name at the top, and a note at the bottom.
Here are a few important paper formatting changes: * Running head is only required for professional (not student) papers * Only a single space should be placed after punctuation. * The new style version endorses the use of the singular “they” as an option for a gender neutral pronoun. * The 7th edition promotes the use of “they” as a singular, gender-neutral pronoun. * In addition to the paper title, author name, and institutional affiliation, a cover page for a student paper should also have the course, instructor name, and due date
American Psychological Association. (2020). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.). https://doi.org/101037/0000165-000
Updated March 10, 2020
Edited and written by Elise Barbeau and Michele Kirschenbaum. Elise is a citation expert and has her master’s degree in public history/library science. She has experience in digital marketing, libraries, and publishing. Michele is a certified library media specialist who loves citations and teaching. She’s been writing about citing sources since 2014.